Humeral Shaft Fractures
Overview
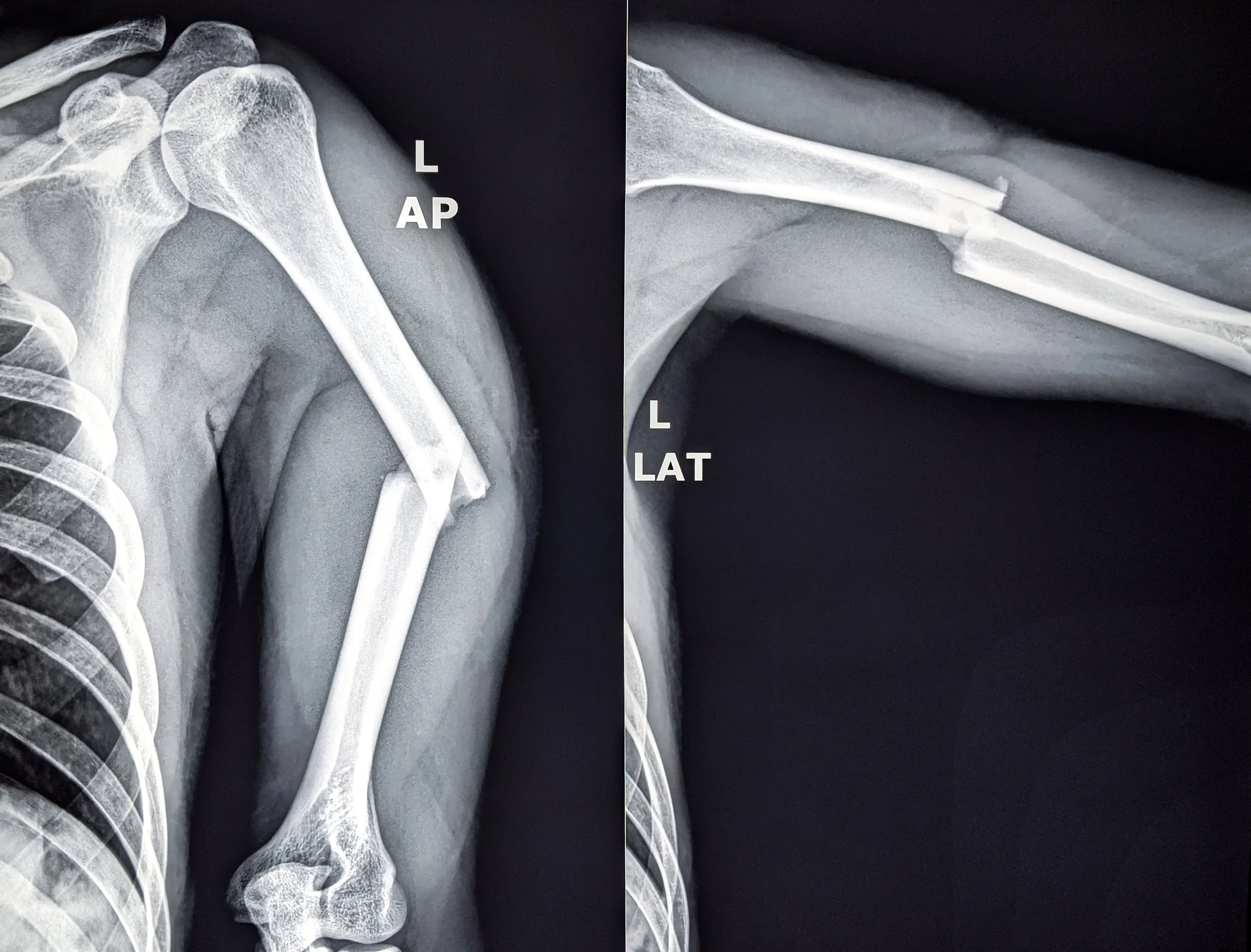
For patients in Richmond, VA seeking specialized care, understanding the mechanics of humeral shaft fractures is the first step toward recovery. This is a break in the long, cylindrical mid-section of the upper arm bone. It usually occurs as a result of serious trauma such as a car accident or a significant fall. It is a unique injury because the radial nerve spirals directly against the back of the bone in this region and can be affected by this fracture. This nerve controls your ability to extend your wrist and fingers. Fortunately, many of these injuries can be treated without surgery, even if they heal somewhat misaligned, as an arm can oftentimes still function very well even if not perfectly straight on an xray.
To make this diagnosis, an x-ray or your humerus is always required.
Symptoms
Pain: Severe pain in the mid-arm.
Instability: The arm feels floppy or unattached in the middle.
Wrist Drop: Inability to give a "thumbs up" or lift the wrist is a sign of a radial nerve palsy that may have occurred with the fracture.
Non-Operative Management
Sarmiento Bracing: A functional clamshell brace that compresses the muscles around the bone. The gentle pressure helps align and hold the fracture. This is highly successful but requires strict compliance and time.
When is Surgery Needed?
Significant fracture misalignment: A high degree of angulation is very well tolerated by patients but if a bone is too angulated, surgery is required to restore future function.
Radial Nerve Entrapment: If the nerve is trapped between bone fragments.
Other associated injuries: If the patient has other fractures in the arm or legs, or if there is any injury to the skin, blood vessels or nerves around the fracture site
Failure of Bracing: If the bone is not healing after a few months.
Surgical Solutions
Humeral Shaft Fixation – Using a metal plate and screws on, or a metal rod inside of, the humerus to realign it and provide immediate stability.